코드공유
지난 글에서는 SQL 데이터베이스와 채팅할 수 있는 간단한 애플리케이션을 만들었습니다. 이 글을 계속 진행하기 전에 여기에서 확인해 보세요.
또한 여기에서 이 코드의 전체 리포지토리를 받으세요.
이전과 지금 글의 차이점
이전 글에서 구축한 애플리케이션은 OpenAI의 토큰 제한으로 인해 매우 큰 데이터베이스에서 제대로 작동하지 않습니다. 데이터베이스가 너무 크면 프롬프트에 전체 열 및 테이블 목록을 콘텍스트로 전송할 수 없습니다. 이 글에서는 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해 노력하겠습니다.
이전 글에서 이미 만든 가장 간단한 애플리케이션의 코드부터 시작해 보겠습니다. 아래 코드는 SQL 데이터베이스에 연결하여 채팅을 시작할 수 있는 간단한 간소화된 애플리케이션을 시작합니다.
import streamlit as st
import requests
import os
import pandas as pd
from uuid import uuid4
import psycopg2
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.chat import SystemMessage, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAI, AzureOpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI, AzureChatOpenAI
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
folders_to_create = ['csvs']
# Check and create folders if they don't exist
for folder_name in folders_to_create:
if not os.path.exists(folder_name):
os.makedirs(folder_name)
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' created.")
else:
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' already exists.")
## load the API key from the environment variable
load_dotenv()
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
llm = OpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
chat_llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key, temperature=0.4)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
def get_basic_table_details(cursor):
cursor.execute("""SELECT
c.table_name,
c.column_name,
c.data_type
FROM
information_schema.columns c
WHERE
c.table_name IN (
SELECT tablename
FROM pg_tables
WHERE schemaname = 'public'
);""")
tables_and_columns = cursor.fetchall()
return tables_and_columns
def save_db_details(db_uri):
unique_id = str(uuid4()).replace("-", "_")
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
tables_and_columns = get_basic_table_details(cursor)
## Get all the tables and columns and enter them in a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(tables_and_columns, columns=['table_name', 'column_name', 'data_type'])
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df.to_csv(filename_t, index=False)
cursor.close()
connection.close()
return unique_id
def generate_template_for_sql(query, table_info, db_uri):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
f"DB connection string is {db_uri}"
f"Here is a detailed description of the table(s): "
f"{table_info}"
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
return answer.content
def get_the_output_from_llm(query, unique_id, db_uri):
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in df['table_name']:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'
return generate_template_for_sql(query, table_info, db_uri)
def execute_the_solution(solution, db_uri):
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
_,final_query,_ = solution.split("```")
final_query = final_query.strip('sql')
cursor.execute(final_query)
result = cursor.fetchall()
return str(result)
# Function to establish connection and read metadata for the database
def connect_with_db(uri):
st.session_state.db_uri = uri
st.session_state.unique_id = save_db_details(uri)
return {"message": "Connection established to Database!"}
# Function to call the API with the provided URI
def send_message(message):
solution = get_the_output_from_llm(message, st.session_state.unique_id, st.session_state.db_uri)
result = execute_the_solution(solution, st.session_state.db_uri)
return {"message": solution + "\n\n" + "Result:\n" + result}
# ## Instructions
st.subheader("Instructions")
st.markdown(
"""
1. Enter the URI of your RDS Database in the text box below.
2. Click the **Start Chat** button to start the chat.
3. Enter your message in the text box below and press **Enter** to send the message to the API.
"""
)
# Initialize the chat history list
chat_history = []
# Input for the database URI
uri = st.text_input("Enter the RDS Database URI")
if st.button("Start Chat"):
if not uri:
st.warning("Please enter a valid database URI.")
else:
st.info("Connecting to the API and starting the chat...")
chat_response = connect_with_db(uri)
if "error" in chat_response:
st.error("Error: Failed to start the chat. Please check the URI and try again.")
else:
st.success("Chat started successfully!")
# Chat with the API (a mock example)
st.subheader("Chat with the API")
# Initialize chat history
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
# Display chat messages from history on app rerun
for message in st.session_state.messages:
with st.chat_message(message["role"]):
st.markdown(message["content"])
# React to user input
if prompt := st.chat_input("What is up?"):
# Display user message in chat message container
st.chat_message("user").markdown(prompt)
# Add user message to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
# response = f"Echo: {prompt}"
response = send_message(prompt)["message"]
# Display assistant response in chat message container
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
st.markdown(response)
# Add assistant response to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
# Run the Streamlit app
if __name__ == "__main__":
st.write("This is a simple Streamlit app for starting a chat with an RDS Database.")프롬프트를 단축하는 기본 아이디어는 프롬프트에서 사용자의 쿼리와 관련된 테이블 및 열 이름만 전송하는 것입니다.
이를 위해 테이블 및 열 이름의 임베딩을 생성하고 사용자의 메시지와 가장 관련성이 높은 이름을 즉석에서 검색하여 프롬프트에 전달할 수 있습니다.
이 글에서는 벡터 데이터베이스로 ChromaDB를 사용하지만 Pinecone, Milvus 또는 다른 데이터베이스를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이제 chromadb를 설치해 보겠습니다.
pip install chromadb먼저 테이블 및 열 이름의 임베딩을 저장할 CSV와 함께 벡터라는 이름의 폴더를 하나 더 만들고, 다른 테이블을 조인하는 외래 키가 무엇인지, 어디 절에 들어갈 수 있는 값의 일부와 같은 데이터베이스에 대한 다른 정보도 저장할 수 있습니다.
def create_vectors(filename, persist_directory):
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=filename, encoding="utf8")
data = loader.load()
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(data, embedding=embeddings, persist_directory=persist_directory)
vectordb.persist()또한 사용자의 쿼리에 테이블에 대한 정보가 필요한지 아니면 데이터베이스의 일반적인 스키마에 대해서만 질문하는 것인지 먼저 확인합니다.
def check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"In the text given text user is asking a question about database "
f"Figure out whether user wants information about database schema or wants to write a SQL query"
f"Answer 'yes' if user wants information about database schema and 'no' if user wants to write a SQL query"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content사용자가 원하는 것에 따라 예 또는 아니요로 대답합니다. 예라고 대답하면 다음과 같은 프롬프트가 생성됩니다.
def prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
"You are an assistant who writes SQL queries."
"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
"Write select query whenever possible"
f"Connection string to this database is {db_uri}"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
다음으로 대답이 '아니요'인 경우 사용자의 쿼리에 매우 구체적으로 테이블의 테이블과 열 이름이 필요하다는 뜻입니다.
이를 위해 먼저 가장 관련성이 높은 테이블과 열을 검색하고 프롬프트에 추가할 문자열을 생성합니다.
벡터가 생성되고 다른 모든 것이 정상적으로 실행되는지 확인해 보겠습니다.
지금까지 작성한 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
import streamlit as st
import requests
import os
import pandas as pd
from uuid import uuid4
import psycopg2
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.chat import SystemMessage, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAI, AzureOpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI, AzureChatOpenAI
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
folders_to_create = ['csvs', 'vectors']
# Check and create folders if they don't exist
for folder_name in folders_to_create:
if not os.path.exists(folder_name):
os.makedirs(folder_name)
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' created.")
else:
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' already exists.")
## load the API key from the environment variable
load_dotenv()
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
llm = OpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
chat_llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key, temperature=0.4)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
def get_basic_table_details(cursor):
cursor.execute("""SELECT
c.table_name,
c.column_name,
c.data_type
FROM
information_schema.columns c
WHERE
c.table_name IN (
SELECT tablename
FROM pg_tables
WHERE schemaname = 'public'
);""")
tables_and_columns = cursor.fetchall()
return tables_and_columns
def create_vectors(filename, persist_directory):
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=filename, encoding="utf8")
data = loader.load()
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(data, embedding=embeddings, persist_directory=persist_directory)
vectordb.persist()
def save_db_details(db_uri):
unique_id = str(uuid4()).replace("-", "_")
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
tables_and_columns = get_basic_table_details(cursor)
## Get all the tables and columns and enter them in a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(tables_and_columns, columns=['table_name', 'column_name', 'data_type'])
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df.to_csv(filename_t, index=False)
create_vectors(filename_t, "./vectors/tables_"+ unique_id)
cursor.close()
connection.close()
return unique_id
def generate_template_for_sql(query, table_info, db_uri):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
f"DB connection string is {db_uri}"
f"Here is a detailed description of the table(s): "
f"{table_info}"
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
return answer.content
def check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"In the text given text user is asking a question about database "
f"Figure out whether user wants information about database schema or wants to write a SQL query"
f"Answer 'yes' if user wants information about database schema and 'no' if user wants to write a SQL query"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
"You are an assistant who writes SQL queries."
"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
"Write select query whenever possible"
f"Connection string to this database is {db_uri}"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def get_the_output_from_llm(query, unique_id, db_uri):
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in df['table_name']:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'
answer_to_question_general_schema = check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query)
if answer_to_question_general_schema == "yes":
return prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri)
return generate_template_for_sql(query, table_info, db_uri)
def execute_the_solution(solution, db_uri):
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
_,final_query,_ = solution.split("```")
final_query = final_query.strip('sql')
cursor.execute(final_query)
result = cursor.fetchall()
return str(result)
# Function to establish connection and read metadata for the database
def connect_with_db(uri):
st.session_state.db_uri = uri
st.session_state.unique_id = save_db_details(uri)
return {"message": "Connection established to Database!"}
# Function to call the API with the provided URI
def send_message(message):
solution = get_the_output_from_llm(message, st.session_state.unique_id, st.session_state.db_uri)
result = execute_the_solution(solution, st.session_state.db_uri)
return {"message": solution + "\n\n" + "Result:\n" + result}
# ## Instructions
st.subheader("Instructions")
st.markdown(
"""
1. Enter the URI of your RDS Database in the text box below.
2. Click the **Start Chat** button to start the chat.
3. Enter your message in the text box below and press **Enter** to send the message to the API.
"""
)
# Initialize the chat history list
chat_history = []
# Input for the database URI
uri = st.text_input("Enter the RDS Database URI")
if st.button("Start Chat"):
if not uri:
st.warning("Please enter a valid database URI.")
else:
st.info("Connecting to the API and starting the chat...")
chat_response = connect_with_db(uri)
if "error" in chat_response:
st.error("Error: Failed to start the chat. Please check the URI and try again.")
else:
st.success("Chat started successfully!")
# Chat with the API (a mock example)
st.subheader("Chat with the API")
# Initialize chat history
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
# Display chat messages from history on app rerun
for message in st.session_state.messages:
with st.chat_message(message["role"]):
st.markdown(message["content"])
# React to user input
if prompt := st.chat_input("What is up?"):
# Display user message in chat message container
st.chat_message("user").markdown(prompt)
# Add user message to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
# response = f"Echo: {prompt}"
response = send_message(prompt)["message"]
# Display assistant response in chat message container
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
st.markdown(response)
# Add assistant response to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
# Run the Streamlit app
if __name__ == "__main__":
st.write("This is a simple Streamlit app for starting a chat with an RDS Database.")벡터가 생성되고 다른 모든 것이 정상적으로 실행되는지 확인
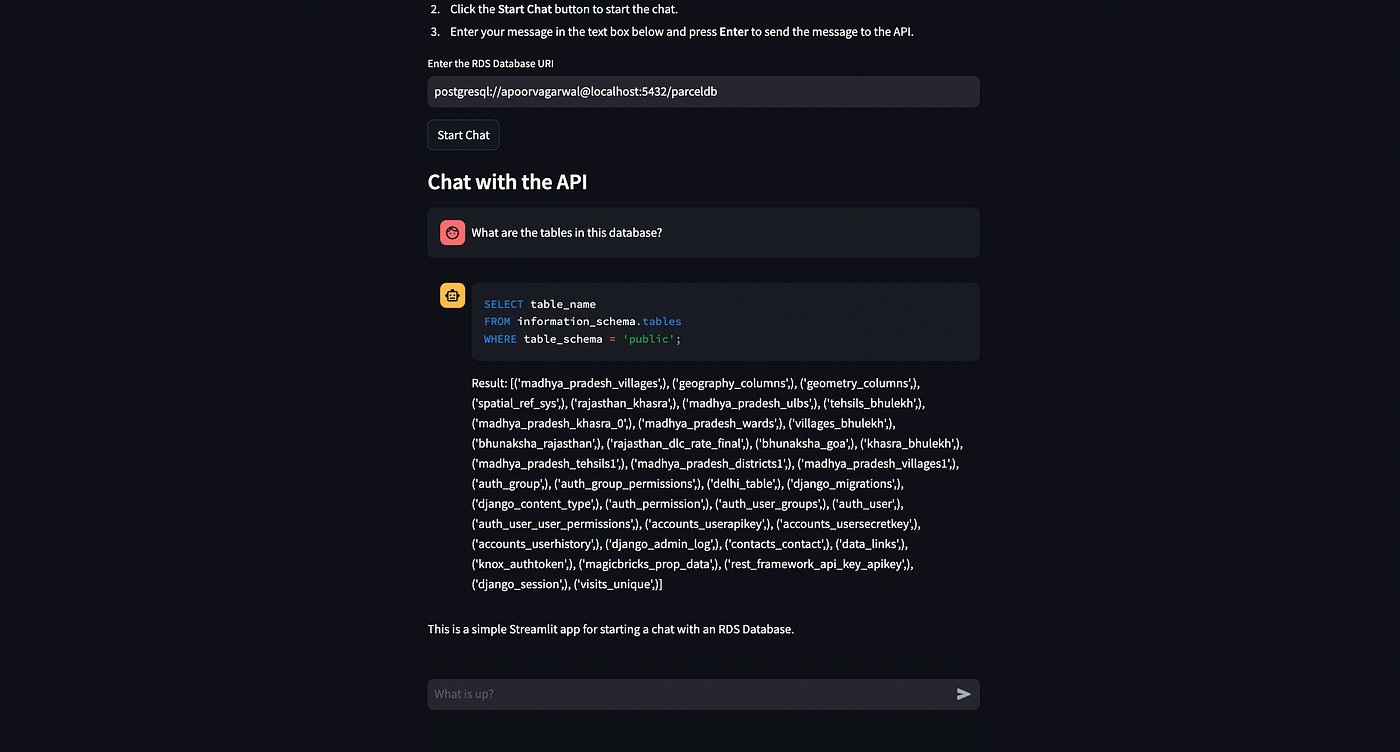
이제 다음 단계에서는 마지막으로 가장 관련성이 높은 테이블의 벡터 검색을 수행하겠습니다.
관련 테이블의 경우 프롬프트에 더 많은 컨텍스트를 제공하기 위해 모든 열을 가져올 것입니다. 마지막으로 이 정보에서 프롬프트에 전달할 문자열을 생성합니다.
vectordb = Chroma(embedding_function=embeddings, persist_directory="./vectors/tables_"+ unique_id)
retriever = vectordb.as_retriever()
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(query)
print(docs)
relevant_tables = []
relevant_tables_and_columns = []
for doc in docs:
table_name, column_name, data_type = doc.page_content.split("\n")
table_name= table_name.split(":")[1].strip()
relevant_tables.append(table_name)
column_name = column_name.split(":")[1].strip()
data_type = data_type.split(":")[1].strip()
relevant_tables_and_columns.append((table_name, column_name, data_type))
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in relevant_tables:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'def generate_template_for_sql(query, relevant_tables, table_info):
tables = ",".join(relevant_tables)
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
f"Assume that there is/are SQL table(s) named '{tables}' "
f"Here is a more detailed description of the table(s): "
f"{table_info}"
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content최종 완성 코드본
Here is the complete code.
import streamlit as st
import requests
import os
import pandas as pd
from uuid import uuid4
import psycopg2
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.chat import SystemMessage, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAI, AzureOpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI, AzureChatOpenAI
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
folders_to_create = ['csvs', 'vectors']
# Check and create folders if they don't exist
for folder_name in folders_to_create:
if not os.path.exists(folder_name):
os.makedirs(folder_name)
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' created.")
else:
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' already exists.")
## load the API key from the environment variable
load_dotenv()
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
llm = OpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
chat_llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key, temperature=0.4)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
def get_basic_table_details(cursor):
cursor.execute("""SELECT
c.table_name,
c.column_name,
c.data_type
FROM
information_schema.columns c
WHERE
c.table_name IN (
SELECT tablename
FROM pg_tables
WHERE schemaname = 'public'
);""")
tables_and_columns = cursor.fetchall()
return tables_and_columns
def create_vectors(filename, persist_directory):
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=filename, encoding="utf8")
data = loader.load()
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(data, embedding=embeddings, persist_directory=persist_directory)
vectordb.persist()
def save_db_details(db_uri):
unique_id = str(uuid4()).replace("-", "_")
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
tables_and_columns = get_basic_table_details(cursor)
## Get all the tables and columns and enter them in a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(tables_and_columns, columns=['table_name', 'column_name', 'data_type'])
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df.to_csv(filename_t, index=False)
create_vectors(filename_t, "./vectors/tables_"+ unique_id)
cursor.close()
connection.close()
return unique_id
# def generate_template_for_sql(query, table_info, db_uri):
# template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
# [
# SystemMessage(
# content=(
# f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
# f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
# f"DB connection string is {db_uri}"
# f"Here is a detailed description of the table(s): "
# f"{table_info}"
# "Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
# )
# ),
# HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
# ]
# )
# answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
# return answer.content
def generate_template_for_sql(query, relevant_tables, table_info):
tables = ",".join(relevant_tables)
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
f"Assume that there is/are SQL table(s) named '{tables}' "
f"Here is a more detailed description of the table(s): "
f"{table_info}"
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"In the text given text user is asking a question about database "
f"Figure out whether user wants information about database schema or wants to write a SQL query"
f"Answer 'yes' if user wants information about database schema and 'no' if user wants to write a SQL query"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
"You are an assistant who writes SQL queries."
"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
"Write select query whenever possible"
f"Connection string to this database is {db_uri}"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def get_the_output_from_llm(query, unique_id, db_uri):
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in df['table_name']:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'
answer_to_question_general_schema = check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query)
if answer_to_question_general_schema == "yes":
return prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri)
else:
vectordb = Chroma(embedding_function=embeddings, persist_directory="./vectors/tables_"+ unique_id)
retriever = vectordb.as_retriever()
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(query)
print(docs)
relevant_tables = []
relevant_tables_and_columns = []
for doc in docs:
table_name, column_name, data_type = doc.page_content.split("\n")
table_name= table_name.split(":")[1].strip()
relevant_tables.append(table_name)
column_name = column_name.split(":")[1].strip()
data_type = data_type.split(":")[1].strip()
relevant_tables_and_columns.append((table_name, column_name, data_type))
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in relevant_tables:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'
return generate_template_for_sql(query, relevant_tables, table_info)
def execute_the_solution(solution, db_uri):
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
_,final_query,_ = solution.split("```")
final_query = final_query.strip('sql')
cursor.execute(final_query)
result = cursor.fetchall()
return str(result)
# Function to establish connection and read metadata for the database
def connect_with_db(uri):
st.session_state.db_uri = uri
st.session_state.unique_id = save_db_details(uri)
return {"message": "Connection established to Database!"}
# Function to call the API with the provided URI
def send_message(message):
solution = get_the_output_from_llm(message, st.session_state.unique_id, st.session_state.db_uri)
result = execute_the_solution(solution, st.session_state.db_uri)
return {"message": solution + "\n\n" + "Result:\n" + result}
# ## Instructions
st.subheader("Instructions")
st.markdown(
"""
1. Enter the URI of your RDS Database in the text box below.
2. Click the **Start Chat** button to start the chat.
3. Enter your message in the text box below and press **Enter** to send the message to the API.
"""
)
# Initialize the chat history list
chat_history = []
# Input for the database URI
uri = st.text_input("Enter the RDS Database URI")
if st.button("Start Chat"):
if not uri:
st.warning("Please enter a valid database URI.")
else:
st.info("Connecting to the API and starting the chat...")
chat_response = connect_with_db(uri)
if "error" in chat_response:
st.error("Error: Failed to start the chat. Please check the URI and try again.")
else:
st.success("Chat started successfully!")
# Chat with the API (a mock example)
st.subheader("Chat with the API")
# Initialize chat history
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
# Display chat messages from history on app rerun
for message in st.session_state.messages:
with st.chat_message(message["role"]):
st.markdown(message["content"])
# React to user input
if prompt := st.chat_input("What is up?"):
# Display user message in chat message container
st.chat_message("user").markdown(prompt)
# Add user message to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
# response = f"Echo: {prompt}"
response = send_message(prompt)["message"]
# Display assistant response in chat message container
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
st.markdown(response)
# Add assistant response to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
# Run the Streamlit app
if __name__ == "__main__":
st.write("This is a simple Streamlit app for starting a chat with an RDS Database.")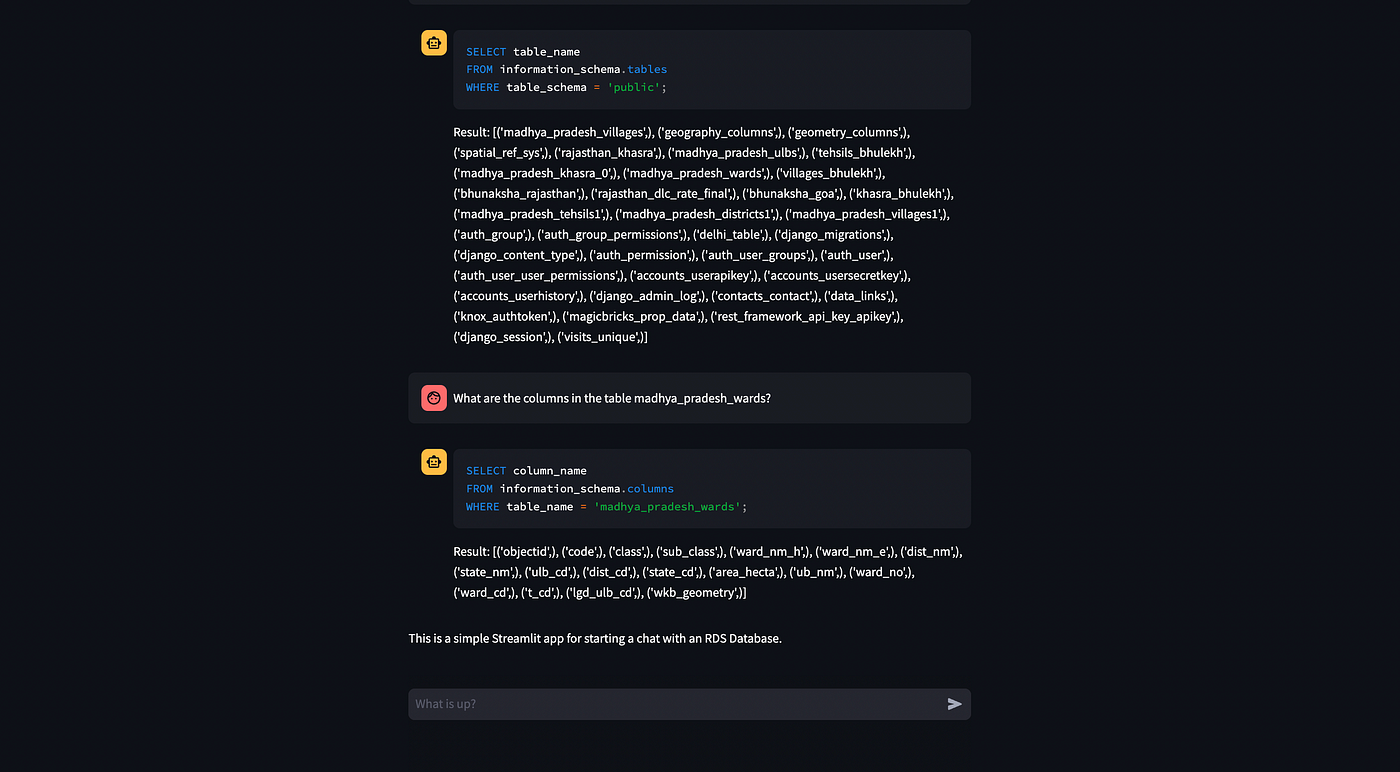
One final thing we can do is to give information about foreign keys to the prompt.
import streamlit as st
import requests
import os
import pandas as pd
from uuid import uuid4
import psycopg2
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.chat import SystemMessage, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAI, AzureOpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI, AzureChatOpenAI
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
folders_to_create = ['csvs', 'vectors']
# Check and create folders if they don't exist
for folder_name in folders_to_create:
if not os.path.exists(folder_name):
os.makedirs(folder_name)
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' created.")
else:
print(f"Folder '{folder_name}' already exists.")
## load the API key from the environment variable
load_dotenv()
openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
llm = OpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
chat_llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key, temperature=0.4)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=openai_api_key)
def get_basic_table_details(cursor):
cursor.execute("""SELECT
c.table_name,
c.column_name,
c.data_type
FROM
information_schema.columns c
WHERE
c.table_name IN (
SELECT tablename
FROM pg_tables
WHERE schemaname = 'public'
);""")
tables_and_columns = cursor.fetchall()
return tables_and_columns
def get_foreign_key_info(cursor):
query_for_foreign_keys = """SELECT
conrelid::regclass AS table_name,
conname AS foreign_key,
pg_get_constraintdef(oid) AS constraint_definition,
confrelid::regclass AS referred_table,
array_agg(a2.attname) AS referred_columns
FROM
pg_constraint
JOIN
pg_attribute AS a1 ON conrelid = a1.attrelid AND a1.attnum = ANY(conkey)
JOIN
pg_attribute AS a2 ON confrelid = a2.attrelid AND a2.attnum = ANY(confkey)
WHERE
contype = 'f'
AND connamespace = 'public'::regnamespace
GROUP BY
conrelid, conname, oid, confrelid
ORDER BY
conrelid::regclass::text, contype DESC;
"""
cursor.execute(query_for_foreign_keys)
foreign_keys = cursor.fetchall()
return foreign_keys
def create_vectors(filename, persist_directory):
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=filename, encoding="utf8")
data = loader.load()
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(data, embedding=embeddings, persist_directory=persist_directory)
vectordb.persist()
def save_db_details(db_uri):
unique_id = str(uuid4()).replace("-", "_")
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
tables_and_columns = get_basic_table_details(cursor)
## Get all the tables and columns and enter them in a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(tables_and_columns, columns=['table_name', 'column_name', 'data_type'])
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df.to_csv(filename_t, index=False)
create_vectors(filename_t, "./vectors/tables_"+ unique_id)
## Get all the foreign keys and enter them in a pandas dataframe
foreign_keys = get_foreign_key_info(cursor)
df = pd.DataFrame(foreign_keys, columns=['table_name', 'foreign_key', 'foreign_key_details', 'referred_table', 'referred_columns'])
filename_fk = 'csvs/foreign_keys_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df.to_csv(filename_fk, index=False)
cursor.close()
connection.close()
return unique_id
# def generate_template_for_sql(query, table_info, db_uri):
# template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
# [
# SystemMessage(
# content=(
# f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
# f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
# f"DB connection string is {db_uri}"
# f"Here is a detailed description of the table(s): "
# f"{table_info}"
# "Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
# )
# ),
# HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
# ]
# )
# answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
# return answer.content
def generate_template_for_sql(query, relevant_tables, table_info, foreign_key_info):
tables = ",".join(relevant_tables)
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"You are an assistant that can write SQL Queries."
f"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
f"Assume that there is/are SQL table(s) named '{tables}' "
f"Here is a more detailed description of the table(s): "
f"{table_info}"
"Here is some information about some relevant foreign keys:"
f"{foreign_key_info}"
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
f"In the text given text user is asking a question about database "
f"Figure out whether user wants information about database schema or wants to write a SQL query"
f"Answer 'yes' if user wants information about database schema and 'no' if user wants to write a SQL query"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri):
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(
content=(
"You are an assistant who writes SQL queries."
"Given the text below, write a SQL query that answers the user's question."
"Prepend and append the SQL query with three backticks '```'"
"Write select query whenever possible"
f"Connection string to this database is {db_uri}"
)
),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"),
]
)
answer = chat_llm(template.format_messages(text=query))
print(answer.content)
return answer.content
def get_the_output_from_llm(query, unique_id, db_uri):
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in df['table_name']:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'
answer_to_question_general_schema = check_if_users_query_want_general_schema_information_or_sql(query)
if answer_to_question_general_schema == "yes":
return prompt_when_user_want_general_db_information(query, db_uri)
else:
vectordb = Chroma(embedding_function=embeddings, persist_directory="./vectors/tables_"+ unique_id)
retriever = vectordb.as_retriever()
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(query)
print(docs)
relevant_tables = []
relevant_tables_and_columns = []
for doc in docs:
table_name, column_name, data_type = doc.page_content.split("\n")
table_name= table_name.split(":")[1].strip()
relevant_tables.append(table_name)
column_name = column_name.split(":")[1].strip()
data_type = data_type.split(":")[1].strip()
relevant_tables_and_columns.append((table_name, column_name, data_type))
## Load the tables csv
filename_t = 'csvs/tables_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename_t)
## For each relevant table create a string that list down all the columns and their data types
table_info = ''
for table in relevant_tables:
table_info += 'Information about table' + table + ':\n'
table_info += df[df['table_name'] == table].to_string(index=False) + '\n\n\n'
## Load the foreign keys csv
filename_fk = 'csvs/foreign_keys_' + unique_id + '.csv'
df_fk = pd.read_csv(filename_fk)
## If table from relevant_tables above lies in refered_table or table_name in df_fk, then add the foreign key details to a string
foreign_key_info = ''
for i, series in df_fk.iterrows():
if series['table_name'] in relevant_tables:
text = table + ' has a foreign key ' + series['foreign_key'] + ' which refers to table ' + series['referred_table'] + ' and column(s) ' + series['referred_columns']
foreign_key_info += text + '\n\n'
if series['referred_table'] in relevant_tables:
text = table + ' is referred to by table ' + series['table_name'] + ' via foreign key ' + series['foreign_key'] + ' and column(s) ' + series['referred_columns']
foreign_key_info += text + '\n\n'
return generate_template_for_sql(query, relevant_tables, table_info, foreign_key_info)
def execute_the_solution(solution, db_uri):
connection = psycopg2.connect(db_uri)
cursor = connection.cursor()
_,final_query,_ = solution.split("```")
final_query = final_query.strip('sql')
cursor.execute(final_query)
result = cursor.fetchall()
return str(result)
# Function to establish connection and read metadata for the database
def connect_with_db(uri):
st.session_state.db_uri = uri
st.session_state.unique_id = save_db_details(uri)
return {"message": "Connection established to Database!"}
# Function to call the API with the provided URI
def send_message(message):
solution = get_the_output_from_llm(message, st.session_state.unique_id, st.session_state.db_uri)
result = execute_the_solution(solution, st.session_state.db_uri)
return {"message": solution + "\n\n" + "Result:\n" + result}
# ## Instructions
st.subheader("Instructions")
st.markdown(
"""
1. Enter the URI of your RDS Database in the text box below.
2. Click the **Start Chat** button to start the chat.
3. Enter your message in the text box below and press **Enter** to send the message to the API.
"""
)
# Initialize the chat history list
chat_history = []
# Input for the database URI
uri = st.text_input("Enter the RDS Database URI")
if st.button("Start Chat"):
if not uri:
st.warning("Please enter a valid database URI.")
else:
st.info("Connecting to the API and starting the chat...")
chat_response = connect_with_db(uri)
if "error" in chat_response:
st.error("Error: Failed to start the chat. Please check the URI and try again.")
else:
st.success("Chat started successfully!")
# Chat with the API (a mock example)
st.subheader("Chat with the API")
# Initialize chat history
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
# Display chat messages from history on app rerun
for message in st.session_state.messages:
with st.chat_message(message["role"]):
st.markdown(message["content"])
# React to user input
if prompt := st.chat_input("What is up?"):
# Display user message in chat message container
st.chat_message("user").markdown(prompt)
# Add user message to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
# response = f"Echo: {prompt}"
response = send_message(prompt)["message"]
# Display assistant response in chat message container
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
st.markdown(response)
# Add assistant response to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
# Run the Streamlit app
if __name__ == "__main__":
st.write("This is a simple Streamlit app for starting a chat with an RDS Database.")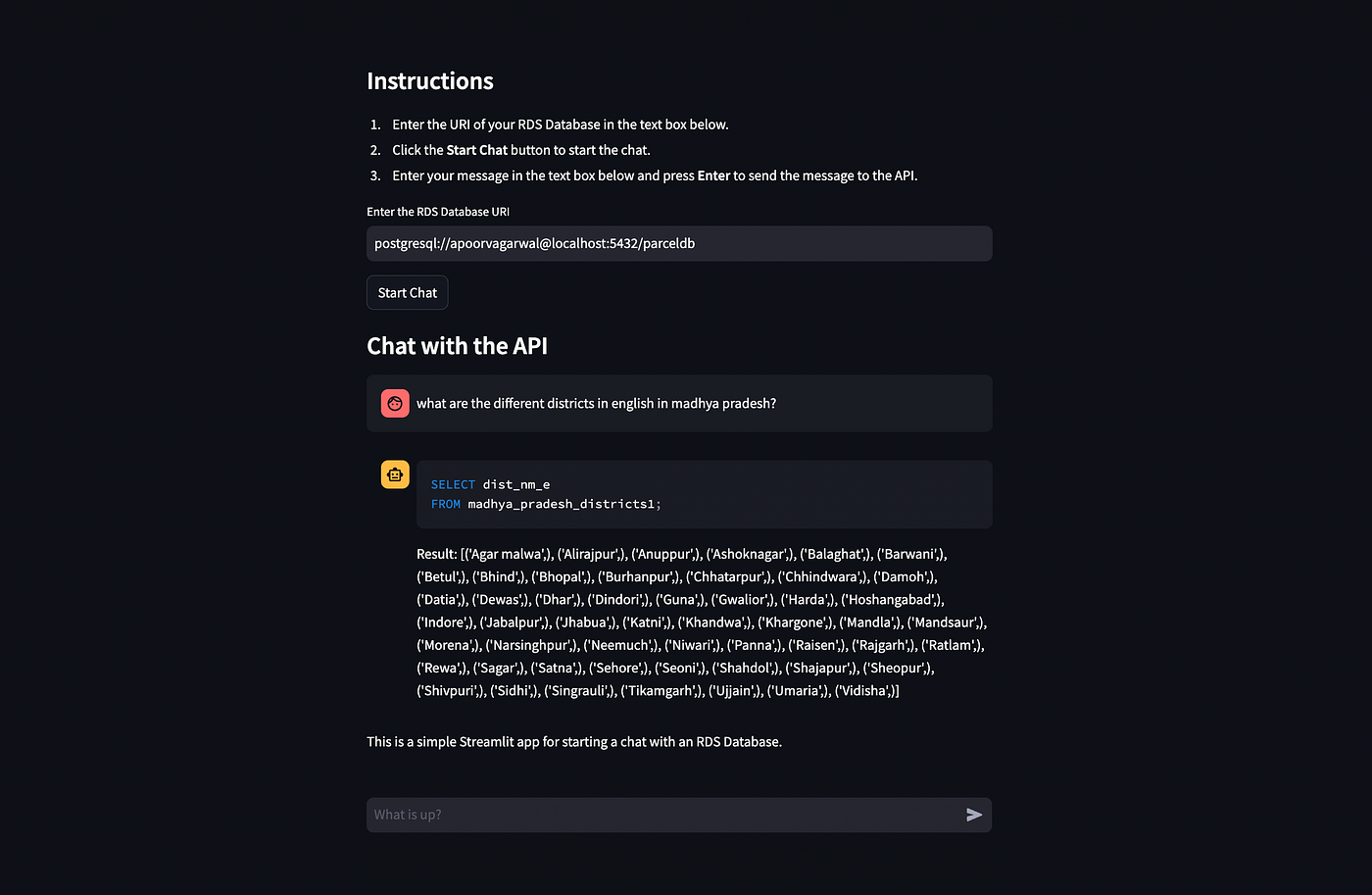
In similar ways we can keep enhancing this application by adding fallbacks. In each fallback we can keep adding additional information.




댓글